Early signs of dementia and cognitive decline
Early signs of dementia and cognitive decline often appear subtly, making them easy to overlook or attribute to normal aging. These changes may include frequent memory lapses, difficulty finding the right words, trouble following conversations, or struggling with familiar tasks. Individuals may also experience confusion about time or place, reduced problem-solving skills, and shifts in mood or personality. Recognizing these early indicators is important, as timely assessment and support can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
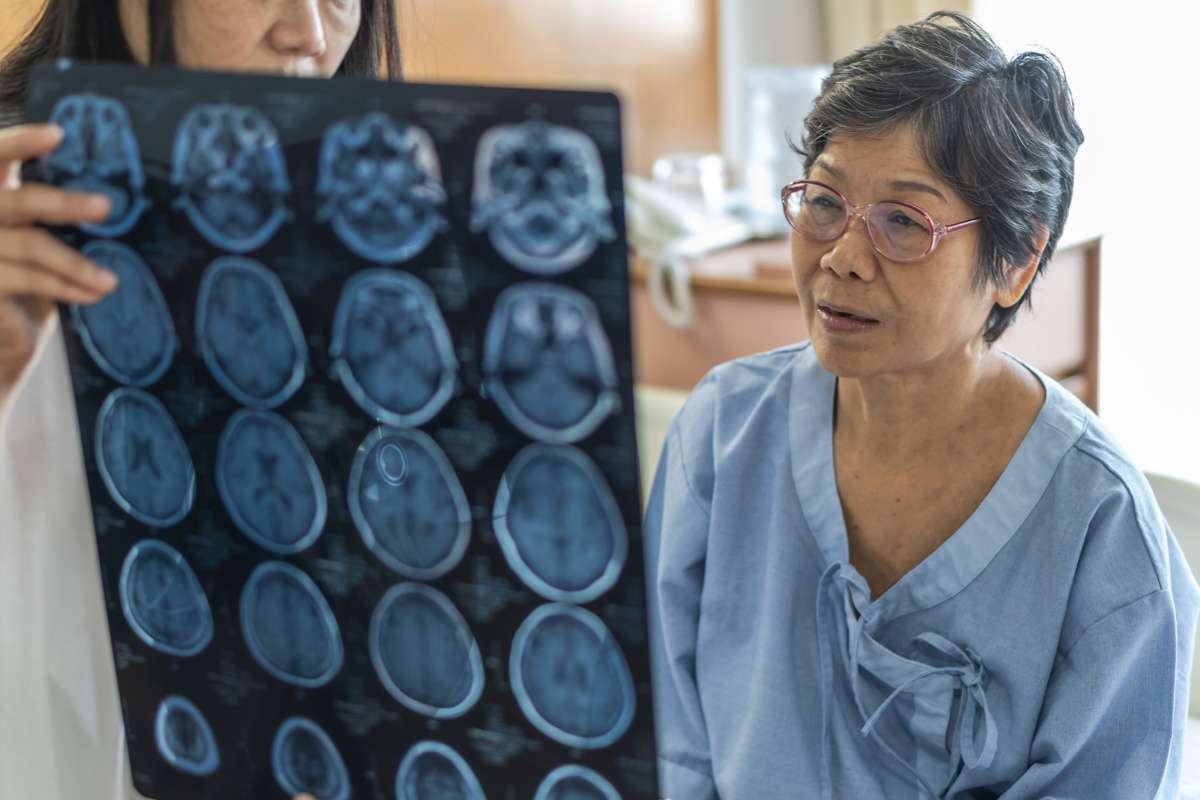
Dementia affects millions of people worldwide, with symptoms that gradually worsen over time. Unlike normal age-related memory changes, dementia significantly interferes with daily life and independence. The condition encompasses various diseases that damage brain cells, with Alzheimer’s disease being the most common form. Early recognition of symptoms allows for better treatment planning and quality of life improvements.
Common Early Symptoms and Warning Signs
The earliest signs of dementia often appear subtly and may be mistaken for normal aging. Memory problems typically manifest first, particularly difficulty remembering recent events, conversations, or appointments. Individuals may repeatedly ask the same questions or forget important dates and events. Other cognitive changes include confusion about time and place, difficulty finding the right words during conversations, and challenges with problem-solving or planning activities.
Changes in judgment and decision-making abilities also emerge early. People may make poor financial decisions, fall victim to scams, or display uncharacteristic behavior in social situations. Mood and personality changes are common, including increased anxiety, depression, or irritability. Some individuals become withdrawn from social activities they previously enjoyed.
Risk Factors and Contributing Causes
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing dementia, though having risk factors doesn’t guarantee the condition will occur. Age remains the strongest risk factor, with chances doubling approximately every five years after age 65. Genetics play a role, particularly for early-onset dementia, though most cases aren’t directly inherited.
Lifestyle factors significantly influence dementia risk. Cardiovascular health problems, including high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol, increase vulnerability. Physical inactivity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption also contribute to higher risk levels. Educational level and social engagement throughout life appear protective, with mentally stimulating activities potentially delaying symptom onset.
Head injuries, particularly repeated trauma, can increase dementia risk later in life. Certain medical conditions, including depression, sleep disorders, and hearing loss, may also contribute to cognitive decline when left untreated.
Importance of Early Detection and Support
Early detection provides numerous advantages for individuals and families facing dementia. Medical evaluation can rule out treatable conditions that mimic dementia symptoms, such as vitamin deficiencies, thyroid problems, or medication side effects. When dementia is confirmed, early diagnosis allows for treatment planning while the person can still participate in decision-making.
Available treatments may slow symptom progression and improve quality of life, though they cannot cure the underlying disease. Medications like cholinesterase inhibitors can help maintain cognitive function for some individuals in early stages. Non-drug interventions, including cognitive stimulation, physical exercise, and social engagement, also show benefits.
| Service Type | Provider Examples | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Memory Assessment | Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic | $500-$2,000 |
| Neuropsychological Testing | Local hospitals, private practices | $1,200-$3,500 |
| Brain Imaging (MRI/PET) | Radiology centers | $1,000-$4,000 |
| Genetic Testing | LabCorp, Quest Diagnostics | $200-$500 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Early detection also enables families to plan for the future while their loved one can express preferences about care, finances, and end-of-life decisions. Legal documents, including advance directives and power of attorney arrangements, are easier to complete when cognitive abilities remain relatively intact.
Support services become more effective when implemented early. Educational programs help families understand what to expect and develop coping strategies. Support groups provide emotional assistance and practical advice from others facing similar challenges. Community resources, including adult day programs and respite care, can extend the time individuals remain in their homes.
Regular medical monitoring allows healthcare providers to adjust treatments as symptoms progress and address complications promptly. This comprehensive approach often results in better outcomes and reduced crisis situations that require emergency interventions.
Recognizing early signs of dementia empowers individuals and families to take proactive steps in managing the condition. While the diagnosis can be overwhelming, early intervention provides the best opportunity for maintaining independence, dignity, and quality of life for as long as possible. Healthcare professionals can guide families through available options and connect them with appropriate resources in their communities.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.