Revolutionizing the Industry: The Latest Trends in Food Processing Machinery
In today’s fast-paced food industry, efficiency, safety, and quality are more critical than ever. Food processing machinery has become the backbone of modern production, enabling manufacturers to streamline operations, reduce waste, and meet the growing demand for packaged and processed foods. From advanced mixers and automated cutting machines to high-speed packaging lines, the latest innovations are transforming kitchens and factories alike—helping businesses stay competitive while ensuring that consumers enjoy fresh, safe, and consistently high-quality products.
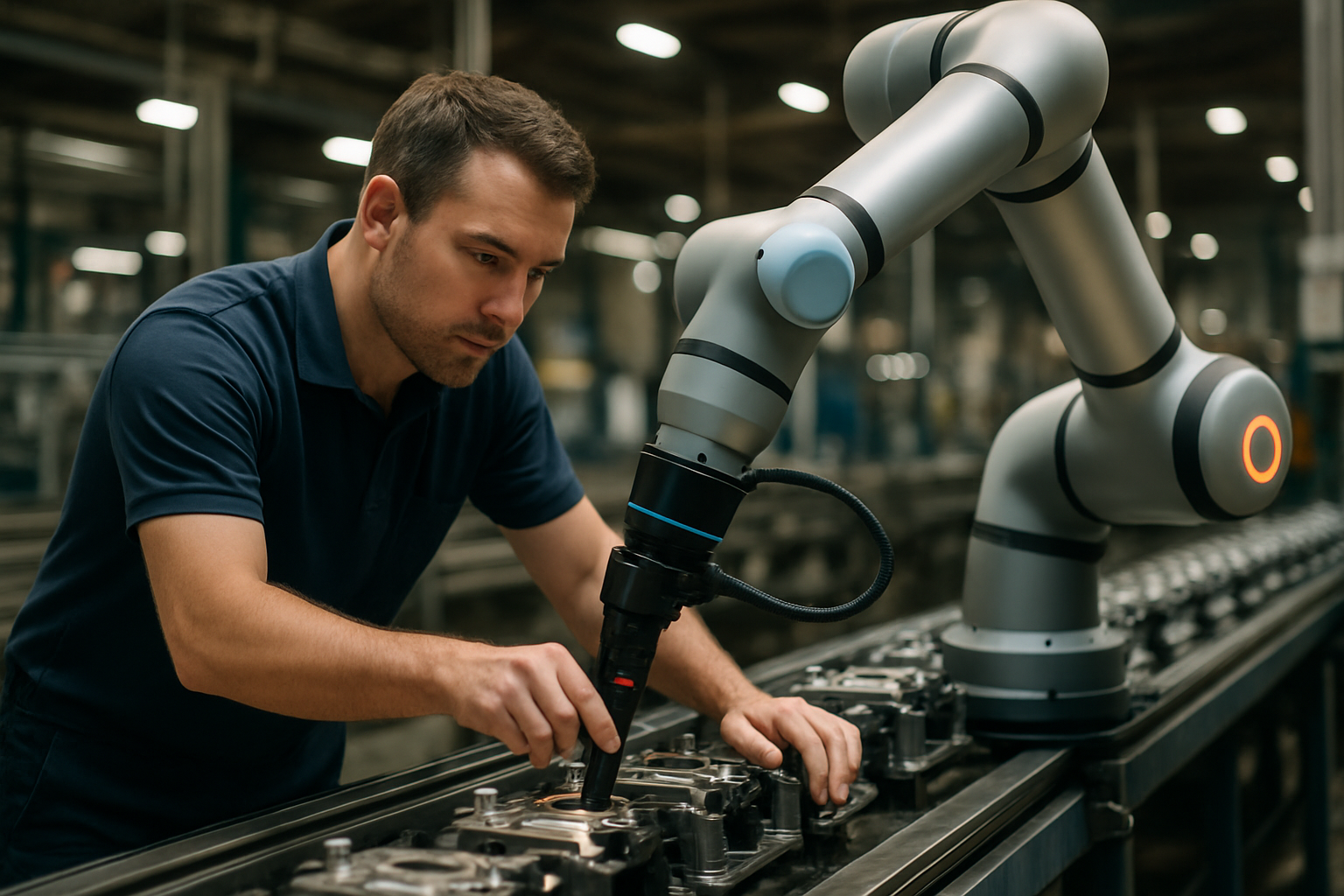

Key Types of Food Processing Machinery and Their Applications
Food processing encompasses a diverse range of equipment designed for specific functions across the production chain. Thermal processing equipment, including ovens, pasteurizers, and sterilizers, ensures food safety by eliminating harmful microorganisms while preserving nutritional value. Size reduction machinery such as slicers, dicers, and grinders transform raw ingredients into appropriately sized components for further processing or packaging. Meanwhile, separation equipment like centrifuges, filters, and extractors isolate desired components from raw materials.
Mixing and blending machinery creates uniform product consistency, while forming equipment shapes products into their final configurations. Packaging machinery completes the production cycle by containing, preserving, and preparing products for distribution. Each category serves specific applications across different food sectors – from meat processing and bakery production to beverage manufacturing and dairy operations. The right selection of equipment depends on product specifications, production volume requirements, and quality standards that manufacturers must maintain.
Benefits of Modern Food Processing Equipment for Businesses
The adoption of advanced food processing machinery offers substantial advantages for businesses seeking to remain competitive in today’s market. Perhaps most significant is the dramatic increase in production efficiency – modern systems can process larger volumes at higher speeds with minimal human intervention. This optimization directly translates to reduced labor costs and increased throughput, allowing manufacturers to meet growing consumer demands.
Quality consistency represents another critical benefit, as automated systems maintain precise control over processing parameters, ensuring uniform products batch after batch. Enhanced food safety is achieved through equipment designed with hygiene in mind, featuring clean-in-place systems, sanitary materials, and designs that eliminate contamination risks. Additionally, modern machinery typically offers improved energy efficiency, reducing utility costs while supporting sustainability initiatives. The flexibility to adjust production lines quickly for different products or batch sizes enables manufacturers to respond agilely to changing market demands – a crucial capability in today’s consumer-driven marketplace.
Emerging Trends and Innovations Shaping the Future of Food Processing
The future of food processing machinery is being defined by several revolutionary trends. Industry 4.0 integration represents a paradigm shift, with smart machines equipped with sensors collecting real-time data to optimize operations, predict maintenance needs, and provide valuable insights into production metrics. These connected systems enable remote monitoring and control, enhancing operational flexibility and responsiveness.
Automation and robotics continue to advance, with collaborative robots (cobots) working alongside human operators to handle repetitive tasks while improving precision and consistency. Artificial intelligence applications are growing, with machine learning algorithms optimizing processes based on vast datasets and predictive analytics anticipating equipment failures before they occur.
Sustainability innovations address growing environmental concerns, with equipment designed for reduced water consumption, energy efficiency, and minimal waste generation. Alternative processing technologies, including high-pressure processing, pulsed electric fields, and ohmic heating, are gaining traction for their ability to preserve nutritional content while ensuring food safety without traditional heat treatments. The versatility of modern equipment also supports the clean label movement, allowing manufacturers to process foods with fewer additives and preservatives while maintaining quality and shelf life.
Cost Considerations for Modern Food Processing Equipment
Investing in advanced food processing machinery requires careful financial planning. Initial acquisition costs vary significantly based on technology sophistication, capacity, and customization requirements. Entry-level processing equipment typically starts at $50,000-$100,000, while comprehensive automated production lines can reach several million dollars. Beyond the purchase price, businesses must consider installation expenses, facility modifications, staff training, and potential production downtime during implementation.
| Equipment Category | Price Range (USD) | Key Cost Factors | ROI Timeframe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Processing | $75,000-$500,000 | Capacity, energy efficiency, automation level | 2-5 years |
| Size Reduction | $30,000-$250,000 | Precision, throughput, material handling | 1-3 years |
| Packaging Systems | $100,000-$1,500,000 | Speed, versatility, integration capabilities | 3-7 years |
| Complete Processing Lines | $500,000-$5,000,000+ | Scale, automation, customization | 3-10 years |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Operating costs present another significant consideration, including energy consumption, maintenance requirements, replacement parts, and specialized technician support. However, modern equipment typically delivers significant return on investment through increased productivity, reduced labor costs, improved yield, and enhanced product quality. Many manufacturers find that advanced machinery pays for itself within 2-5 years, depending on utilization rates and production volumes. Additionally, financing options including leasing, equipment loans, and phased implementation strategies can make these investments more accessible for businesses of various sizes.
The Impact of Food Processing Machinery on Product Innovation
Advanced processing equipment has become a catalyst for product innovation across the food industry. Manufacturers now possess the technical capabilities to develop novel textures, flavors, and formulations that were previously impossible. For example, extrusion technology has revolutionized plant-based protein products, creating meat alternatives with remarkably similar textural properties. Precision portioning and forming equipment enable consistent, unique product shapes that enhance brand recognition and consumer appeal.
Beyond product development, modern machinery supports the growing demand for personalized nutrition and functional foods. Equipment designed for gentle processing preserves bioactive compounds, while precision dosing systems ensure accurate incorporation of nutrients, probiotics, and other functional ingredients. The flexibility of contemporary processing lines also facilitates rapid prototyping and small-batch production, allowing manufacturers to test new concepts in the market with minimal financial risk. As consumer preferences continue to evolve, the adaptability of processing equipment will remain a crucial competitive advantage for food manufacturers seeking to innovate and differentiate their offerings.
The ongoing revolution in food processing machinery represents a confluence of technological innovation, market demands, and operational optimization. As the industry continues to evolve, manufacturers who strategically invest in these advanced systems will be best positioned to meet changing consumer preferences, navigate regulatory requirements, and maintain competitive advantage in an increasingly complex global marketplace.