Revolutionizing Health: How Glucose Monitoring Smartwatches Are Transforming Diabetes Management
Glucose monitoring smartwatches are changing the way people manage diabetes by offering continuous, real-time tracking of blood sugar levels directly from the wrist. These innovative devices combine convenience with advanced technology, allowing users to monitor trends, receive alerts for high or low glucose, and make informed lifestyle or medication adjustments instantly. Beyond diabetes management, they empower individuals to take proactive control of their overall health, bridging the gap between medical care and everyday life.
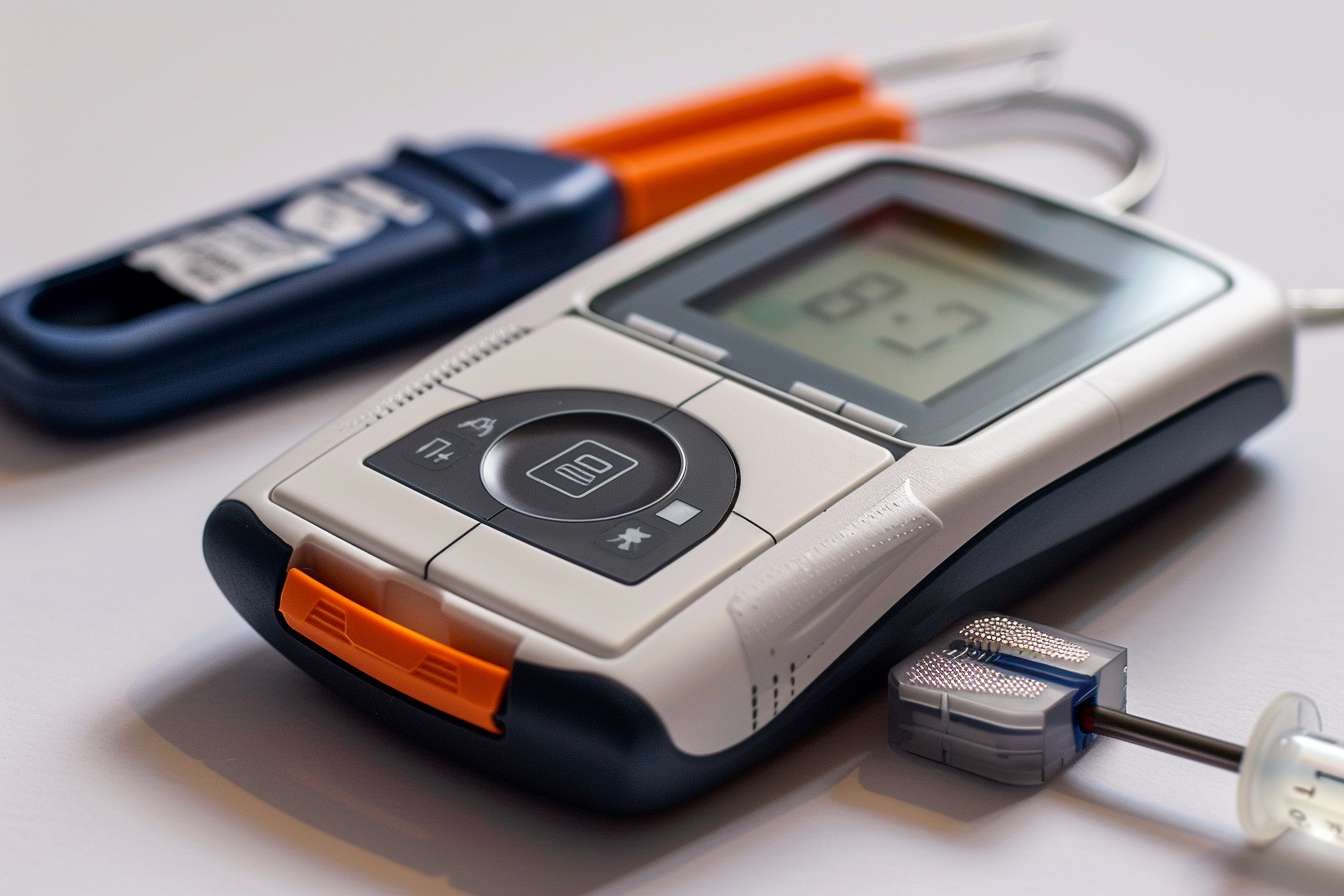
How Glucose Monitoring Smartwatches Work
Glucose monitoring smartwatches utilize different technologies to measure blood glucose levels without traditional finger pricks. Most contemporary devices employ either minimally invasive or non-invasive methods. Minimally invasive systems typically use tiny sensors inserted just under the skin that measure glucose in interstitial fluid—the fluid surrounding cells. These sensors communicate wirelessly with the smartwatch, which displays readings and tracks patterns over time.
Non-invasive technologies are advancing rapidly, with some watches using optical sensors that measure glucose through the skin using specific light wavelengths. Others employ microwave technology or measure glucose in sweat or other bodily fluids. The watch processes this data using algorithms that convert the readings into useful information displayed on the watch face or companion smartphone app, allowing users to view their glucose levels at a glance.
Benefits for Diabetes Management and Daily Health
The integration of glucose monitoring into smartwatches offers numerous advantages for diabetes management. Continuous monitoring provides a comprehensive picture of glucose fluctuations throughout the day, helping identify patterns that might be missed with traditional spot-checking methods. This comprehensive data helps users understand how specific foods, activities, stress levels, and medications affect their glucose levels in real-time.
Many glucose monitoring smartwatches include alert systems that notify users when their glucose levels fall outside predetermined ranges. These timely alerts can prevent dangerous hypoglycemic episodes before they become severe. Additionally, the data collected can be shared directly with healthcare providers, enabling more informed treatment decisions and adjustments to care plans without requiring extra office visits.
Beyond diabetes management, these devices often incorporate other health metrics like heart rate, sleep quality, and physical activity tracking, offering a more holistic view of health. This comprehensive approach helps users understand the interconnections between different aspects of their health and lifestyle choices, potentially leading to better overall health management.
Current Glucose Monitoring Smartwatch Technologies
Several technologies currently power the glucose monitoring capabilities in smartwatches available on the market. Each approach offers different advantages in terms of accuracy, convenience, and user experience. Understanding these differences can help consumers make informed choices about which technology best suits their needs.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems paired with smartwatches represent one of the most accurate approaches currently available. These systems typically use a small sensor inserted under the skin that communicates with the smartwatch. While technically these involve two devices working together, the integration is becoming increasingly seamless, with data displayed directly on the watch face.
Other watches use optical sensors similar to those used for heart rate monitoring, but calibrated to detect glucose levels. While generally less accurate than CGM systems, these non-invasive approaches are improving rapidly and offer the advantage of complete non-invasiveness. Some emerging technologies use microwave or radio wave technology, measuring the reflection of these waves as they interact with glucose molecules in blood vessels near the skin’s surface.
Market Availability and Device Comparison
The market for glucose monitoring smartwatches continues to expand with various options available to consumers with different needs and preferences. These devices range from those focused specifically on glucose monitoring to more comprehensive health watches with integrated glucose features.
| Device | Monitoring Technology | Key Features | Estimated Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple Watch (with compatible CGM) | Works with external CGM sensors | Health ecosystem integration, ECG, activity tracking | $399-$799 plus CGM costs |
| Fitbit Sense 2 (with CGM compatibility) | Works with partner CGM systems | Stress management, sleep tracking, heart health metrics | $299-$399 plus CGM costs |
| K’Watch Glucose | Microwave/enzymatic patch technology | Direct glucose reading without separate sensor | $99-$199 (subscription needed) |
| GlucoWatch (prototype) | Non-invasive optical sensing | No sensor required, direct reading | Not yet commercially available |
| Freestyle Libre + smartwatch app | NFC-enabled sensor patch | 14-day wear sensor, smartphone/watch integration | $60-$75 per sensor + device cost |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The Future of Wearable Health Technology
The glucose monitoring smartwatch market is poised for significant evolution in coming years. Research teams worldwide are working on improving non-invasive monitoring accuracy to match that of traditional methods. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are being integrated to provide predictive capabilities—warning users of potential glucose fluctuations before they occur based on historical patterns and current conditions.
Future iterations of these devices will likely see increased integration with insulin delivery systems, potentially creating closed-loop systems that automatically adjust insulin levels based on glucose readings—essentially functioning as an artificial pancreas. This technology could dramatically reduce the mental burden on patients who currently must make constant calculations and adjustments throughout the day.
The integration of glucose monitoring with other health metrics will continue to evolve, creating more comprehensive health management tools. As these technologies become more affordable and accessible, they may eventually become standard preventive health tools—not just for those with diagnosed diabetes but for anyone interested in metabolic health monitoring and disease prevention.
Glucose monitoring smartwatches represent a significant step forward in diabetes management technology, offering convenience, continuous data, and improved quality of life for those managing the condition. As technology continues to advance, these devices will likely become more accurate, affordable, and integrated with broader health monitoring systems—ultimately transforming diabetes from a condition requiring constant manual monitoring to one that can be managed more seamlessly within daily life.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.